How to Charge
Plug in electric vehicles at home. If you’re on the go and need to charge up the battery, find a charging station at many locations throughout the United States and Canada. Most charging networks have downloadable apps to easily find locations when you're on-the-go.
Charging Levels
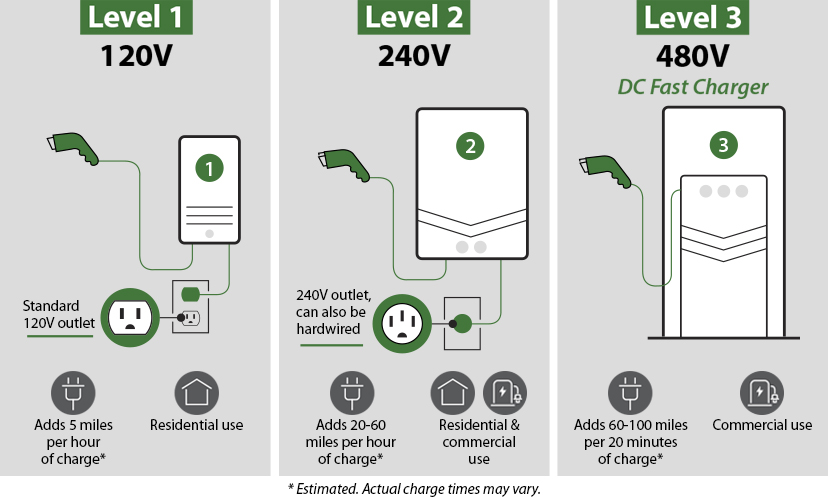
Level 1 Charging
- Home charging
- Requires a grounded (three-prong) standard residential 120V outlet
- Suitable for low- and medium-range plug-in hybrids
- Suitable for all-electric battery electric vehicle drivers with low daily driving usage
- Adds 5 miles per hour
Level 2 Charging
- Home and public charging
- Typically requires a charging unit on a 240V outlet, like one used to power an electric clothes dryer
- May require a service upgrade by a certified electrician
- The 240V outlet charges in about half the time it takes to charge at a 120V outlet
- Most common public chargers
- Public Level 2 chargers have a standard EV connection plug that fits all current vehicles, except for Teslas, which require an adapter
- Adds 20-60 miles per hour, depending on amps
Level 3 DC Fast Charging
- Fastest charge currently available
- Commercial use
- Adds 60-100 miles per 20 minutes, depending on amps
- Charging at a DCFC station is only effective if your battery state-of-charge (SOC) is below 80 percent. After that point, charging will slow down significantly
How Do I Plug In?
- All home charging options (except Tesla) use a universal EV plug (SAE J1772) to connect to the car. The other end of the charging cord can either be hardwired or plugged into an existing outlet.
- Level 2 public chargers also use a universal EV plug (SAE J1772)
- Level 3/DCFC chargers offer one of three unique plug types: CHAdeMO (Nissan & Mitsubishi), SAE CCS (US and European auto makers), and Tesla.
Before driving to a public charging station, it is important to know:
- The difference between Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 charging stations.
- The type of connector compatible with your EV before planning a trip.


